Updated: 7/8/2020
My first lab was Johan’s hydration kit. It’s incredibly powerful, customizable, and educational. Unfortunately it takes a little more time and know-how than a novice like myself was initially prepared for.
However, at MMS Steve Jesok pointed out that Microsoft provides an all-in-one solution: the Windows and Office Deployment Lab Kit. Within minutes, we can have a fully functional domain controller and MEMCM server.
The Requirements
-
Set up a host device - For this lab, I’m using a Windows 10 Pro workstation with an old i7 CPU, 16GB of RAM, and a secondary 500GB hard drive.
-
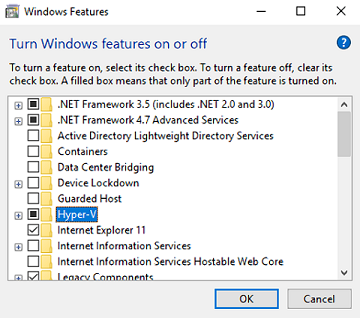
Enable Hyper-V - If Hyper-V is not yet installed, open Turn Windows features on or off, check Hyper-V, and click OK. Reboot.
-
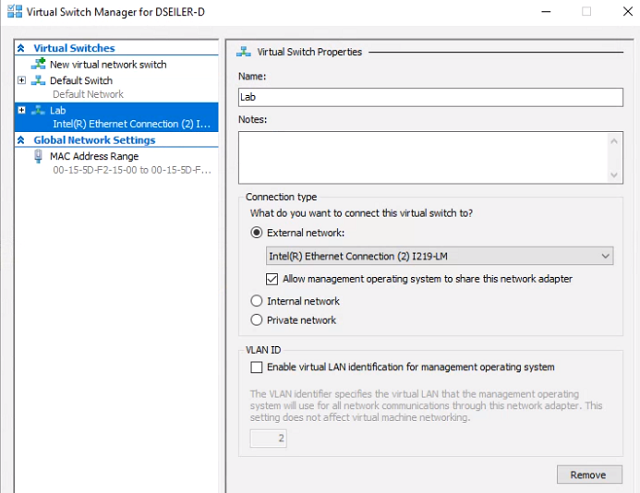
Configure networking - Launch Hyper-V as administrator, and open the Virtual Switch Manager. Under Virtual Switches, select New virtual network switch. Select External and click Create Virtual Switch. Name it Lab and and leave everything else default. Click OK, and if you are prompted with a warning, click OK again.
The Setup
-
Download the kit from the link above. It has the virtual machines and step-by-step documentation on how to configure services. This is the only thing we need to download.
-
Extract the lab zip file, preferably to a drive that is large and fast.
-
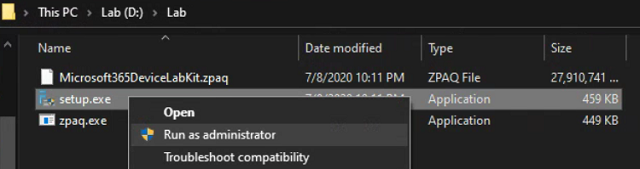
Install - Right click Setup.exe and run as administrator. If prompted by SmartScreen, click More Info and then click Run anyway.
-
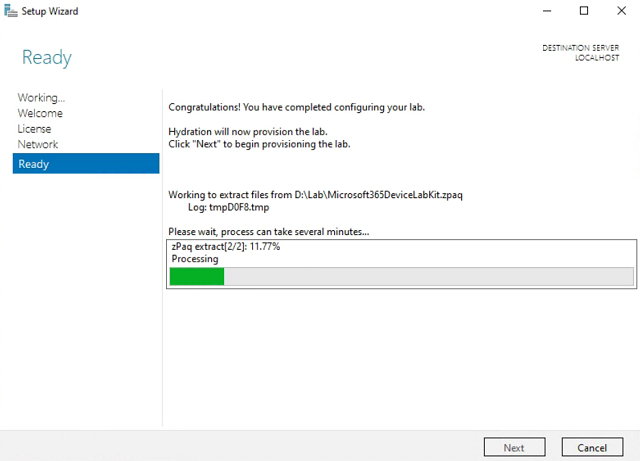
Setup Wizard - Click Next all the way through to the end. It will import all the VMs into Hyper-V.
-
Configure VM Settings - You should see HYD-DC1 and HYD-GW1 already running. Shut them down. We won’t be using HYD-GW1 again.
-
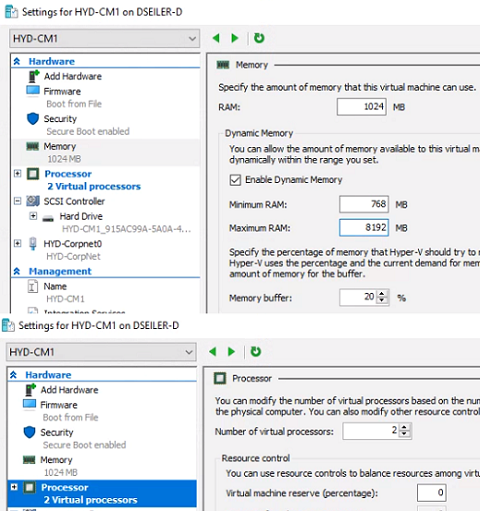
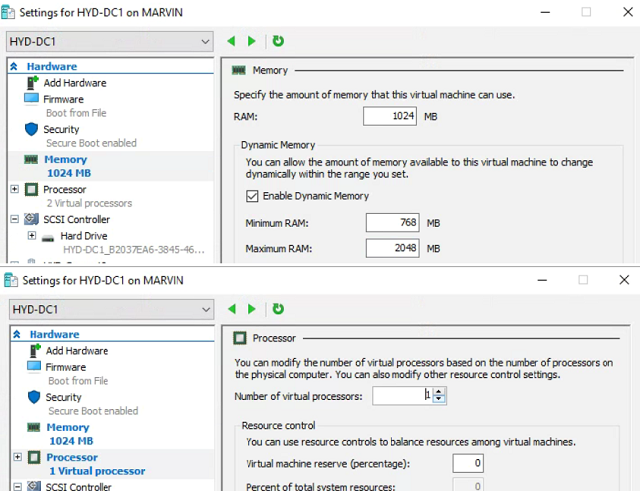
Domain Controller - Right click HYD-DC1 and select Settings. Set Maximum Memory to 2048MB and leave Enable Dynamic Memory checked. Set CPU to one virtual processor.
-
MEMCM Server - Right click HYD-CM1 and select Settings. Leave memory settings at default. Set CPU to two virtual processors.
NAT Networking
Note: We will NOT be using the external virtual switch called Lab from Step 3 of the Requirements section. It was only necessary so that Setup.exe from the Setup section would run.
-
NAT Networking - We’ll use Ami Arwidmark’s NAT network script instead of the Internet Gateway (HYD-GW1) to make the lab simpler. You can learn more about NAT networking here.
-
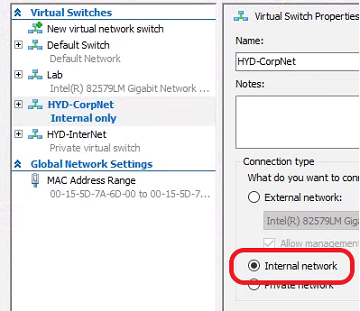
Prepare the Virtual Switch - The Deployment Lab Kit creates it’s own private network switch, so we need to make it an Internal one to work with Ami’s script. In Hyper-V click Virtual Switch Manager. Click on HYD-CorpNet. Select Internal network and click OK.
- Customize the script - On the host system, launch Windows Powershell ISE as Administrator. Copy and paste the following code into the top script pane. This is an edited version of Ami’s code customized for our Microsoft lab. Hit F5 to run it.
New-NetIPAddress –IPAddress 10.0.0.254 -PrefixLength 24 -InterfaceAlias "vEthernet (HYD-CorpNet)" New-NetNat –Name HYD-CorpNetNATNetwork –InternalIPInterfaceAddressPrefix 10.0.0.0/24 - We now have our host Windows 10 OS performing NAT on the internal virtual switch HYD-CorpNet. Our VMs are already pointing to it as the default gateway.
The Test
-
Power on HYD-DC1 and wait for the log on screen. This is so our servers and workstations can talk to Active Directory.
-
Power on HYD-CM1 and log in. The passwords for the local administrator accounts and for CORP\LabAdmin is P@ssw0rd
-
Confirm the MEMCM server has internet access by launching command prompt and pinging 8.8.8.8.
-
Give HYD-CM1 another moment for services to start up. Launch the Microsoft Endpoint Manager Configuration Manager Console and confirm that it loads successfully.
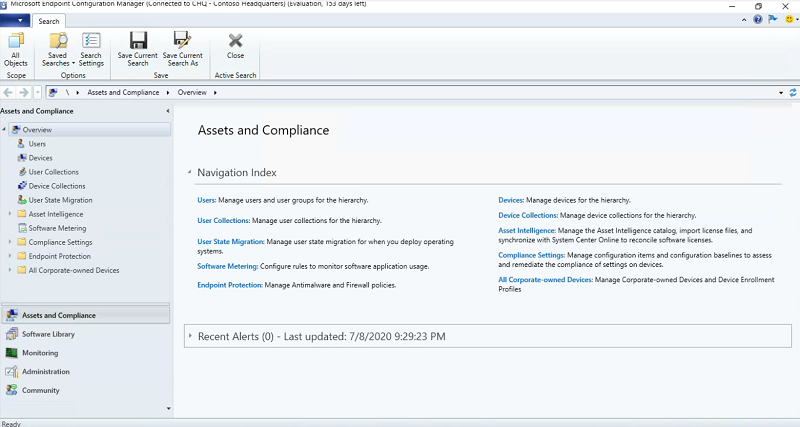
Refer to the troubleshooting section if anything isn’t working at this point
The Finishing Touch
Now that we’ve got a functioning domain, MEMCM server, and internet access, it’s time to update.
-
In the MEMCM console, navigate to the Administration node and select Updates and Servicing. Click on Check for updates.
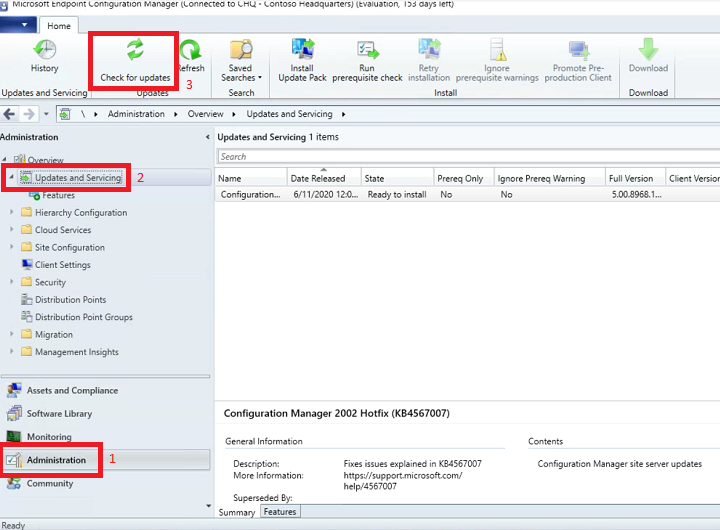
-
If the latest version hasn’t already started downloading, select it (in this case 1902), right click and choose Download.
-
Once it is downloading, on the bottom pane click on the Show Status link.
-
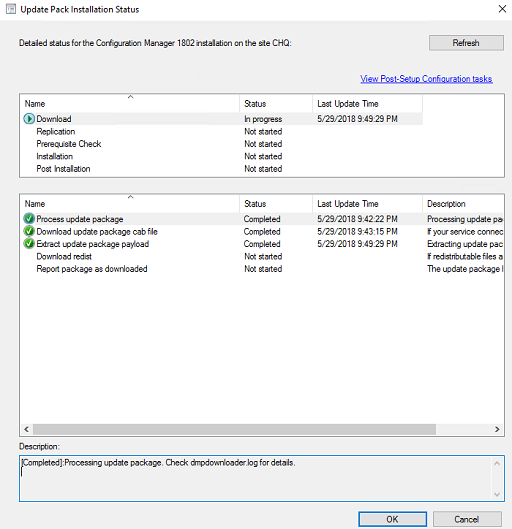
On the Updates and Servicing Status page for our chosen update, right click update package and choose Show Status again.
-
From here, we can follow the download AND installation statuses of the latest MEMCM upgrade.
-
Once the download is complete, go back to the Administration node and click on Updates and Servicing again. The update we downloaded should now say Ready to install.
-
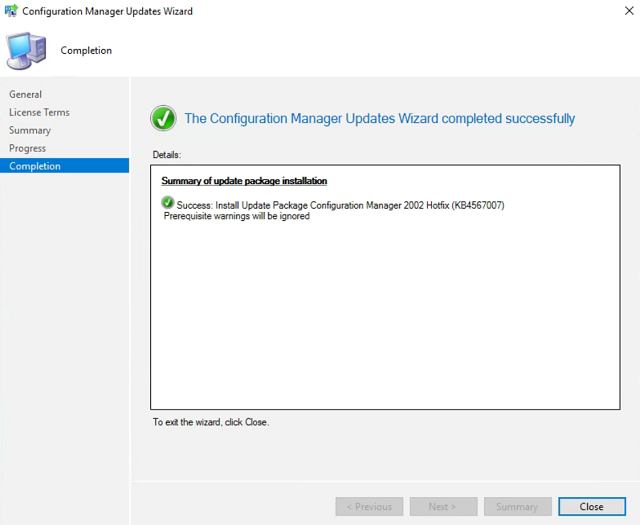
Right click the update and select Install Update Pack. Check Ignore any prerequisite check warnings… and click Next until we reach the License Terms. Check the box, and keep clicking Next until the wizard completes successfully. Click Close.
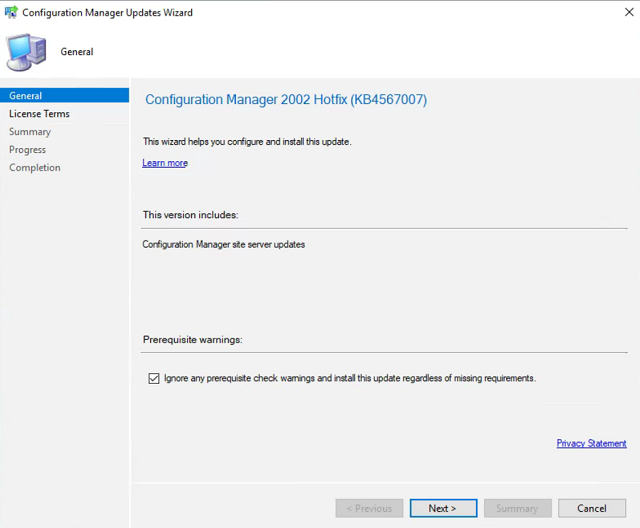
-
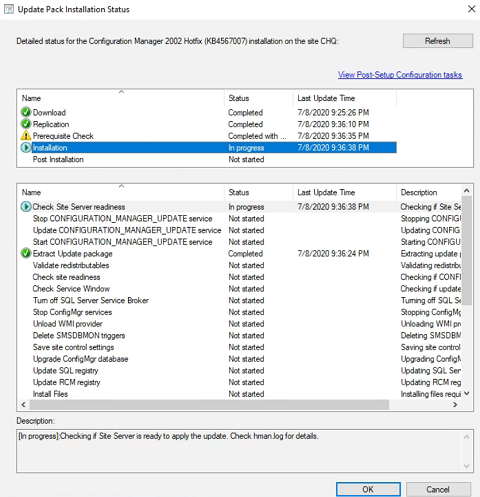
Repeat steps 3 and 4 and watch the update installation progress. Refresh until the Update Wizard is complete and click Close.
-
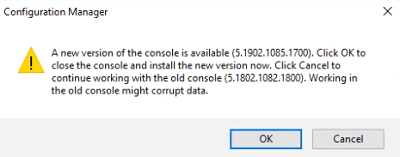
Close the MEMCM console and relaunch it. We will be prompted to upgrade the console to the new version. Click OK, and if prompted for elevation click OK again.
Congratulations! We now have a functional MEMCM environment we can configure and customize.
Next up - Operating System Deployment over PXE
Troubleshooting
If there are any obstacles during set up, we can try some of these troubleshooting tips
- Firewall - If you cannot ping 8.8.8.8, we don’t have access to the internet. From CM1, try pinging DC1 at 10.0.0.6. If that works, try pinging the NAT gateway at 10.0.0.254. If that doesn’t work, try temporarily disabling the firewall as that might be blocking access.
You may need to remove and redo the NAT networking as well, so run the following command in an elevated Powershell terminal:Remove-NetIPAddress -IPAddress 10.0.0.254 Remove-NetNat New-NetIPAddress –IPAddress 10.0.0.254 -PrefixLength 24 -InterfaceAlias "vEthernet (HYD-CorpNet)" New-NetNat –Name HYD-CorpNetNATNetwork –InternalIPInterfaceAddressPrefix 10.0.0.0/24 -
NAT - If you can ping 10.0.0.254 but STILL can’t ping 8.8.8.8, make sure HYD-GW1 is powered off. If it is, the issue is on the host system. From the host system, ping CM1 at 10.0.0.7 to confirm NAT is working. If NAT is working, from CM1 ping the host IP of the physical adapter.
- Subnet - The lab network is 10.0.0.0/24. If our home network is also on 10.0.0.0/24 we’ll have trouble getting out. We will either need to ditch the NAT and rely on GW1, or re-IP DC1 and CM1 and our NAT configuration on a different network. Just keep in mind in subsequent blog posts we’ll need to adjust networking respectively.
For example if you wanted to change the lab from the default 10.0.0.0/24 network to a 10.11.12.0/24 network, change the CM1 IP to 10.11.12.7 and the DC1 IP to 10.11.12.6. Remove the NAT config and make a new one on that network like so:Remove-NetIPAddress -IPAddress 10.0.0.254 Remove-NetNat New-NetIPAddress –IPAddress 10.11.12.254 -PrefixLength 24 -InterfaceAlias "vEthernet (HYD-CorpNet)" New-NetNat –Name HYD-CorpNetNATNetwork –InternalIPInterfaceAddressPrefix 10.11.12.0/24